For years we’ve tried to educate the industry about testing D8-THC properly by avoiding coelution with D9-THC and the isomerization byproducts. Lately, I’ve been asked by several clients to combine D8-THC and D8-iso-THC in our COA reporting. The nomenclature is likely the cause of this, because D8-THC and D8-iso-THC are likely isomers, right? The answer is no.
First, here is an old post showing the analysis of D8-THC to get the separation required to report it independently of D8-iso-THC: GC Separation of iso-THC, D8-THC, and D9-THC Application Note
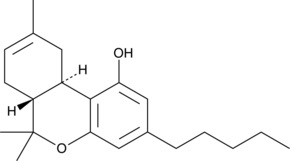
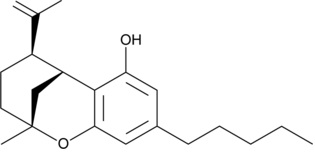
Next, here are the chemical structures of the two substances:
D8-THC
D8-iso-THC
Note they both have the same 5 carbon alkyl chain off the benzene ring, but that’s about it in terms of similarities.
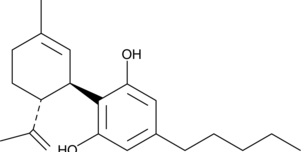
The significant difference is apparent in the open carbon ring of D8-iso-THC compared to the closed carbon ring of D8-THC. In this respect, D8-iso-THC has more in common with CBD than D8-THC.
See CBD here:
That being said, D8-iso-THC does not have psychoactive effects. It is considered to be inert similar to CBD.
Adding D8-iso-THC to D8-THC should not be considered appropriate when analyzing these substances. It is falsely contributing to an overestimation of D8-THC, thus falsely indicating a substance’s COA adding these two together is more psychoactive than a substance not adding them together.
Adding D8-THC and D8-iso-THC for reporting on COAs seems to be the default because many labs still lack the abilities to separate these two non-isomeric substances on HPLC.
If you want higher D8-THC concentrations, make more D8-THC and less D8-iso-THC in your reactions.